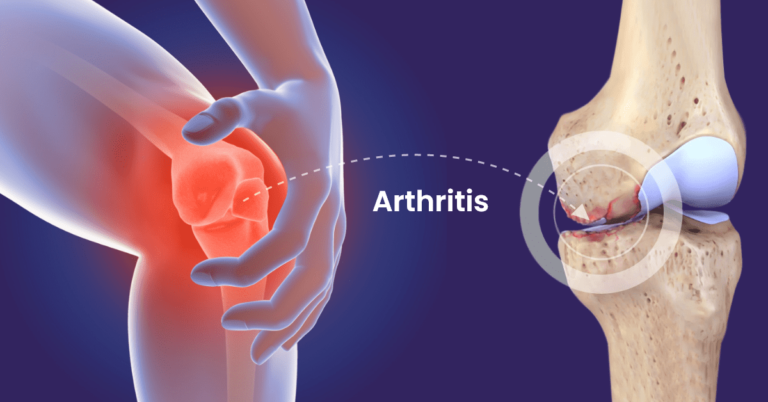
Arthritis is a chronic condition that leads to joint inflammation, causing pain, stiffness, swelling, warmth, redness, and a reduced range of motion. It can affect not only the joints but also the surrounding tissues and, in some cases, other organs like the heart, eyes, or skin. There are more than 150 types of arthritis, each with distinct causes and treatment approaches. Common types include:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common form, often linked to aging or joint overuse.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
- Gout: Typically affects a single joint, most commonly the big toe, and is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals.
Although arthritis currently has no cure, various treatments can help manage symptoms, improve mobility, and prevent further damage. Key treatments include:
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Exercise: Engage in regular, low-impact activities like swimming or walking to strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the joints, particularly weight-bearing ones like the knees and hips.
- Stretching: Gentle stretching exercises help maintain or improve flexibility and joint function.
- Assistive Devices: Tools such as braces, splints, or modified grips can provide joint support and make daily tasks easier.
- Medications:
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These can reduce pain and swelling.
- Prescription medications: Corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics may be prescribed for autoimmune types like rheumatoid arthritis to reduce inflammation and prevent damage.
- Topical treatments: Creams or gels containing anti-inflammatory agents can be applied directly to the skin to help with localized pain.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Occupational Therapy: Techniques and adaptations to help with daily activities and improve quality of life.
- Hydrotherapy: Water-based exercises that reduce pressure on joints while providing resistance.
- Surgery: This is typically considered a last resort when other treatments haven’t provided sufficient relief. Options may include joint replacement, arthroscopy, or synovectomy to remove damaged tissue.
Tips for Managing Arthritis:
- Stay Active, But Listen to Your Body: Regular exercise is key, but avoid overexerting yourself. Opt for low-impact exercises like yoga, swimming, or cycling to protect joints.
- Prioritize Joint Protection: Use ergonomic tools and positions to reduce strain on affected joints. Small adjustments can make a significant difference in daily comfort.
- Incorporate Anti-inflammatory Foods: A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish like salmon), leafy greens, and antioxidants can help reduce inflammation.
- Stay Positive and Seek Support: Arthritis can be emotionally challenging. Connecting with others who have the condition or joining support groups can provide emotional and mental relief.
Starting treatment early can help slow down the progression of arthritis and protect joints from permanent damage, improving long-term outcomes and quality of life.