Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a popular spice and medicinal herb with a long history of use across various cultures for both culinary and therapeutic purposes. This flowering plant, native to Southeast Asia, belongs to the Zingiberaceae family, which also includes turmeric, cardamom, and galangal. The part of the plant most commonly used is the rhizome (underground stem), often referred to as ginger root.
Uses of Ginger:
Ginger is extremely versatile and can be used in various forms, including fresh, dried, powdered, or as juice or oil. It is a common ingredient in cooking, particularly in Asian, Indian, and Middle Eastern cuisines, where it adds a warming, spicy flavor to both sweet and savory dishes. It’s also frequently found in teas, smoothies, and processed foods. Beyond cooking, ginger is used in natural remedies, herbal supplements, and even in skincare products due to its medicinal properties.
Health Benefits of Ginger:
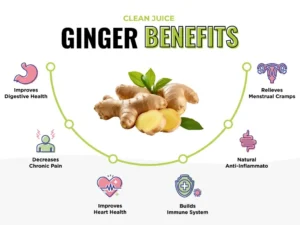
- Supports Digestion: Ginger is renowned for its digestive benefits. It helps reduce bloating and gas by aiding the digestive process. Studies have shown that ginger can break down and expel excess gas in the gastrointestinal tract, providing relief from discomfort. Additionally, ginger stimulates the movement of food and waste through the digestive system, which can help prevent constipation and promote overall gut health.
- Relieves Nausea: One of ginger’s most well-known uses is its ability to reduce nausea. Research indicates that ginger can be effective in managing morning sickness during pregnancy, as well as nausea associated with chemotherapy, motion sickness, and other gastrointestinal issues. It is believed that gingerols (the bioactive compounds in ginger) help alleviate nausea and vomiting. Fresh ginger, dried ginger, and ginger tea have all been found to be particularly effective in reducing nausea.
- Reduces Inflammation: Ginger contains bioactive compounds such as gingerol, which have strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. These properties may help reduce inflammation in conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. By reducing inflammation, ginger can alleviate joint pain and stiffness. Some studies suggest that ginger extract may be a helpful adjunct treatment for managing chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Pain Relief: In addition to reducing inflammation, ginger has analgesic properties that may help alleviate pain. Ginger’s active compounds are believed to interfere with pain-causing molecules in the body, which could explain its effectiveness in reducing pain related to conditions such as menstrual cramps, arthritis, and general body aches.
- Boosts Immune System: Ginger is widely used as a natural remedy for colds and the flu. It has antimicrobial properties that can help combat infections. While much of the evidence supporting this use is anecdotal, some studies suggest that ginger may enhance immune function, particularly by improving the body’s antibody response. A study on smokers found that ginger extract could strengthen immune responses, indicating its potential in supporting the body’s defense system.
- Supports Cardiovascular Health: Ginger may have positive effects on cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of heart disease. Research suggests that regular ginger consumption may help lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve circulation. Additionally, ginger may help reduce oxidative stress, which plays a role in heart disease. Some studies also suggest ginger extract may protect against coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, and hyperlipidemia.
- Helps Prevent Cancer: Ginger is rich in antioxidants, which can help neutralize free radicals in the body and reduce oxidative stress, a key factor in the development of cancer. Some studies have suggested that ginger may inhibit the growth of cancer cells, particularly in cancers of the gastrointestinal system, such as colorectal, pancreatic, gastric, and liver cancers. Though research is still in its early stages, ginger’s anti-cancer properties show promising potential.
- Regulates Blood Sugar and Diabetes Risk: Preliminary research suggests that ginger may have a role in reducing the risk of diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity. A study found that ginger supplementation could help regulate blood sugar levels, which is vital for individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, more research is needed to confirm the full effects of ginger on diabetes management.
How to Use Ginger:
- Fresh Ginger: Peel and grate fresh ginger root to use in cooking, smoothies, or herbal teas. Fresh ginger adds a pungent, spicy flavor to recipes and can be used to prepare ginger tea by boiling it in water.
- Dried Ginger: Dried ginger is often used in baking or added to powdered spice blends. It is a convenient form of ginger, often used to make ginger tea or as a spice in many recipes.
- Ginger Powder: Ginger powder is available commercially and can be used in a wide range of culinary applications. It is commonly added to baked goods, curries, and soups for flavoring and health benefits.
- Ginger Oil: Ginger oil is commonly used in aromatherapy or diluted for topical applications to reduce muscle pain or improve circulation. It is also used in personal care products like lotions and massage oils.
- Ginger Supplements: Ginger capsules or tablets are available for those who want to take ginger as a supplement. These supplements can be used to help with digestive issues, nausea, and inflammation.
How to Grow Ginger:
Ginger grows best in tropical and subtropical climates with plenty of warmth, humidity, and indirect sunlight. It can be grown in pots indoors if the environment is warm enough. To grow ginger, use a fresh ginger rhizome with visible buds (known as eyes). Place it in moist soil, ensuring that the roots are covered, and water regularly. Ginger typically takes 8-10 months to mature and can be harvested by digging up the rhizome.
Countries Where Ginger is Found:
Ginger is native to Southeast Asia, but it is now widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. Major producers include India, China, Indonesia, and Nigeria. It is also grown in parts of the Caribbean, Africa, and Latin America.
Intake Amount and Timing:
The recommended daily intake of ginger can vary depending on the purpose of use. Generally, 1-2 grams of ginger per day is considered safe for most people. For nausea, 0.5-1 gram of ginger is typically effective. It can be consumed in the form of tea, supplements, or added to meals. To avoid side effects, it is advisable not to exceed 4 grams per day.
Precautions:
While ginger is generally safe for most people, excessive consumption may lead to side effects such as heartburn, diarrhea, or irritation of the mouth. Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking ginger, especially in supplement form, as it may interact with certain medications or affect pregnancy.
Conclusion:
Ginger is a powerful herb with a wide range of health benefits, including digestive support, pain relief, anti-inflammatory properties, immune boosting, and potential cancer prevention. Incorporating ginger into your diet can provide numerous health benefits, and its versatility in culinary and medicinal uses makes it an essential addition to any home.



